PCASTL
An interpreted high level programming language which makes writing self-modifying code easier.
Website | Source (Last update 2018)
Its features are:
- The "parent" keyword to access a parent node in the code syntax tree.
- The "childset" keyword to access a child node in the code syntax tree.
- The use of explicit code segments delimited with ` and '.
- Allows calls to dynamic-link libraries, shared object libraries or dynamic libraries.
- Object, array and chained list data types. They are respectively created by internal functions names, array and list.
- ANSI stdio.h interface for single-byte strings functions.
- Turing complete.
For example, inside the interpreter, the tree having its root in the variable fact after the following code has been executed:
fact = function(x)
{
if (x == 1) return(1)
return(x * fact(x - 1))
}
is:
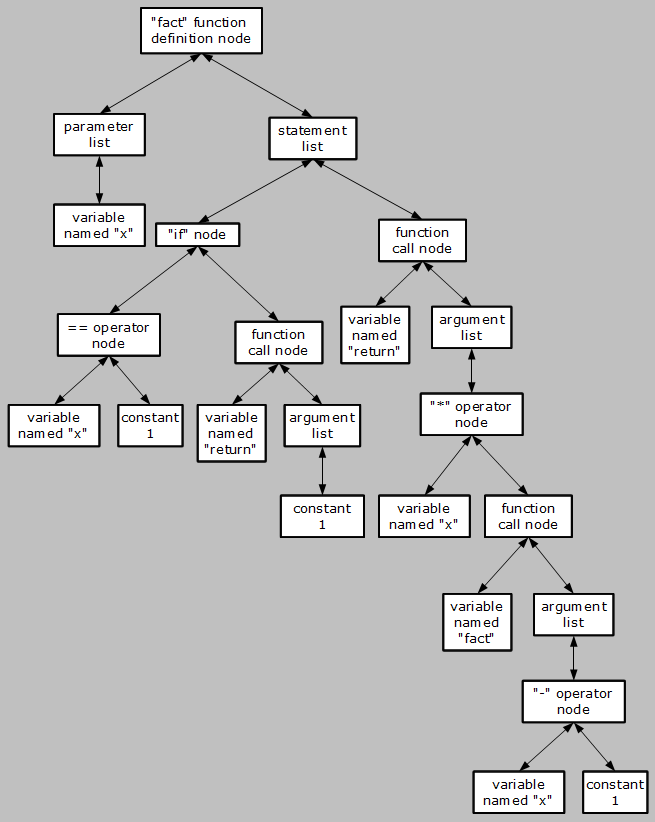
Below you can see how childset and parent keywords can be used to navigate this tree.
> info(fact)
[node_type] "function definition"
[nb_children] 2
[parameters][0] "x"
>
> info(fact.childset[0])
[node_type] "list"
[nb_children] 1
>
> info(fact.childset[0].childset[0])
[node_type] "variable"
[nb_children] 0
[name] "x"
>
> info(fact.childset[1])
[node_type] "list"
[nb_children] 2
>
> info(fact.childset[1].childset[0])
[node_type] "if statement"
[nb_children] 2
>
> info(fact.childset[1].childset[1])
[node_type] "function call"
[nb_children] 2
[nb_args] 1
>
> info(fact.childset[0].parent)
[node_type] "function definition"
[nb_children] 2
[parameters][0] "x"
Here are ways to edit the tree:
> mknode(fact.childset[1], `if (x < 1) {
+ print("Parameter must be greater than zero.")
+ abort()
+ }', 0)
> fact(-2)
"Parameter must be greater than zero."
> info(fact.childset[1])
[node_type] "list"
[nb_children] 3
>
> info(fact.childset[1].childset[0].childset[1].childset[1])
[node_type] "function call"
[nb_children] 2
[nb_args] 0
>
> fact.childset[1].childset[0].childset[1].childset[1] = `return(-1)'
0x431c20
> info(fact.childset[1].childset[0].childset[1].childset[1])
[node_type] "function call"
[nb_children] 2
[nb_args] 1
>
> fact(-2)
"Parameter must be greater than zero."
-1
Tags: language
Last modified 17 February 2026